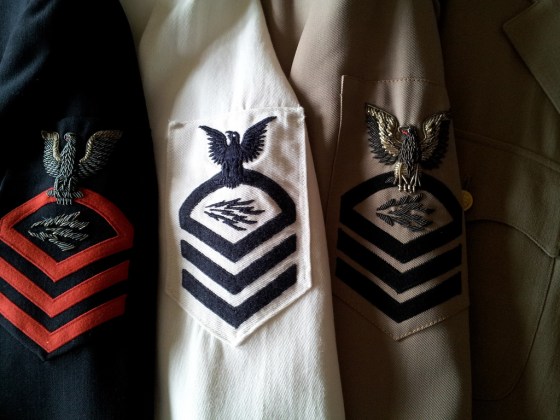
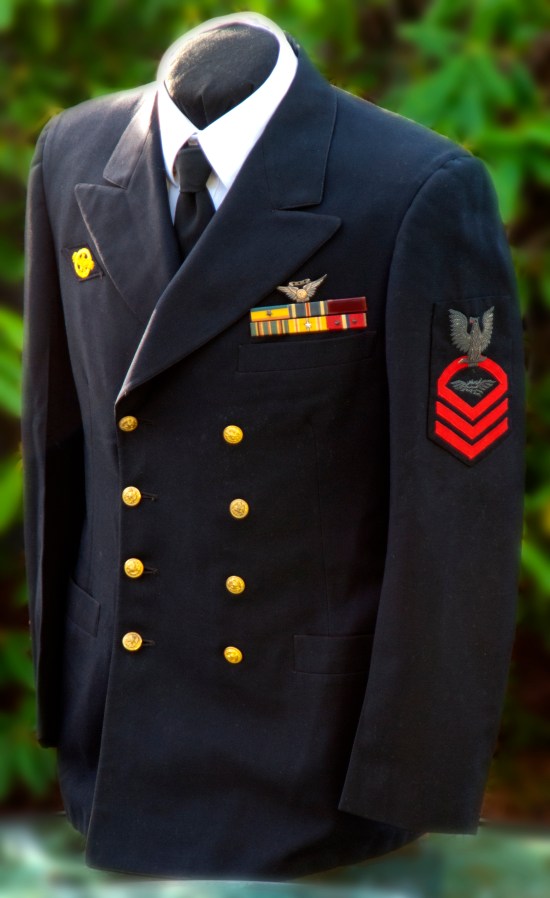
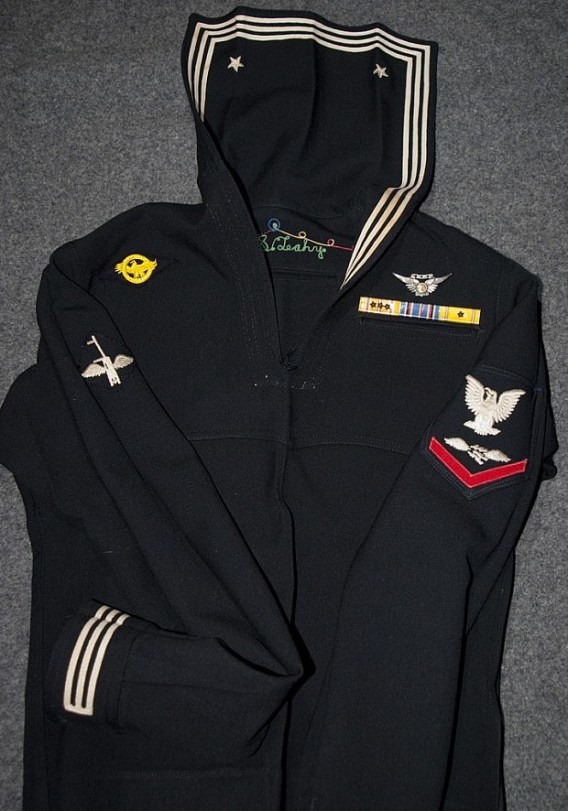
Category Archives: Medals
A Piece of Memphis Belle’s Heart
In the sub-freezing temperatures, you find yourself watching for them. Anxiety has long-since set in and your heart-rate is rapid causing you to draw quick, short breaths from the cold oxygen flowing into your mask. You’re thinking back to the darkness of the early-morning hours, reviewing all of the landmarks as you check the heading. At 35,000 feet, your aluminum tube is barreling ahead, amidst a cloud of familiar shapes, at nearly 200 miles per hour. Your body is no longer aware of the vibrations and deafening roar of the four Wright Cyclone radial engines and their steady drone. You’ve been through this same routine (as if any of this can be considered “routine”) two dozen times before.

Sighting numerous Focke Wolfe 190 fighters was sadly a common occurrence for B-17 crews.
Suddenly, excited chatter is piped directly to your ears via the cold headset. Your fellow crew-members have sprung to life as they call them out – the dreaded camouflage-painted Focke-Wulf Fw 190 bearing the black cross of Germany. The flight of attackers begins to assail the surrounding B-17F aircraft in your group. You reach for the trusty Browning M2 .50 caliber machine gun as you scan the skies for the attackers.
Gripping the handle of the gun with your fleece-lined leather gloves, you begin to train the weapon as you search for the enemy. You try to fight back the fear while looking through the Plexiglas nose, seeing another Flying Fortress rollover into its deadly dive. You don’t have time to look to see if there are any chutes, yet you are hold on to a shred of hope that those men do somehow manage to survive…

The crew of the Memphis Belle pose in front of the aircraft that returned from 25 deadly missions over German-held positions. Captain Evans is pictured, second from the right in the back row.
52,000 Americans perished in the air over Europe during World War II over the span of three and a half years. Contrast that to 58,000 Americans who lost their lives during the entire Vietnam War. It is difficult to imagine that bomber crews had to complete 25 bombing missions before they could be sent home. More than 750,000 bombing sorties were flown by U.S Army Air Force aircraft over Europe and just under 10,000 bombers were lost. The odds were infinitesimal that one aircraft could survive all of those missions and return home during the war. One of those B-17s that achieved that mark was the famed Memphis Belle (Boeing B-17F-10-BO Flying Fortress Serial 41-24485) – the first heavy bomber to do so. The monumental feat was the subject of a William Wyler documentary, Memphis Belle: A Story of a Flying Fortress, released in 1944 to American audiences by Paramount Pictures.
Though I attempted to paint a picture of what it was like for these men, words could never come close to describing that experience. A single mission was harrowing for these amazing men. I often wonder which was more unnerving – the first mission or the twenty-fifth and final one. For Captain Vince Evans, sitting in the bombardier chair for those several harrowing hours on May 19, 1943 on a raid over German port-city of Kiel on the Jutland peninsula.

Many questions surrounded this jacket as to its authenticity. Some collectors were quite doubtful while still others suggested that it was genuine (source: eBay image).
When an item from one the 10-member crew of the Memphis Belle, it certainly doesn’t go unnoticed. A few years ago, what appeared to be a cut-down, tailor-made officers jacket complete with period correct insignia and devices was listed at auction. Inside the jacket was a label with Captain Evan’s personal information, including his Army serial number (ASN). One issue some collectors raised with this listing was the seemingly incorrect ribbon bar. One important piece absent from the bar was Captain Evan’s Distinguished Flying Cross (DFC) ribbon which was awarded to all ten crewmen. Vince would subsequently receive an additional DFC. The ribbon for the Air Medal is also absent devices which Evans would have had to indicate multiple awards.

The Captain Evans jacket label shows his name and service number (source: eBay image).
Regardless of the minor shortcomings, the jacket is believed (by several collectors) to be genuine and was more than likely set aside by Evans after the war in favor of a newer uniform. The correct (or better yet, original) ribbon bar was probably removed (by Evans) for wear on the new uniform.
- The period-correct collar devices are beautifully displayed on the Evans jacket (source: eBay image).
- The Evans jacket has the SSI of the 8th Air Force on the left shoulder (source: eBay image).
- Captain Evans’ bombardier wings and ribbon bar, complete with a ribbon from his Air Medal, American Campaign Medal and his European–African–Middle Eastern Campaign Medal (source: eBay image).
Following his WWII service, Evans began working with Wyler in his new profession as a writer in Hollywood with two films to his credit: Chain Lightning (starring Humphrey Bogart) and Battle Hymn (starring Rock Hudson). Evans served in the USAF Reserve until his discharge (at the rank of major) in 1953. Sadly, Major Evans would perish (along with his wife, Margery and their 21 year-old daughter, Venetia) in a small airplane when it crashed a few miles short of the Santa Ynez Valley airport in 1980. What the Luftwaffe and Nazi anti-aircraft gunnery could not do, a series of atmospheric conditions did. It was never determined who was in control of the aircraft (Evans or the flight instructor) at the time of the crash.
The Memphis “Belle lost one of her sweetest members” wrote Colonel Robert Morgan (in his book, The Man Who Flew the Memphis Belle: Memoir of a WWII Bomber Pilot), “a large piece” of her heart went down that day.
More than 40 bids from buyers eager to land a piece of history so closely-tied to the famed aircraft drove the final sale price to $1,026.97 which for many militaria collectors is a bargain considering the notoriety of the Memphis Belle and her crew.
Learning to Listen to that Quiet Voice of Reason: A Medal That Wasn’t Quite Right
You see the militaria item and at first glance, it looks great. Your heart starts racing as you begin to realize that you’re finally getting your hands one a highly sought-after piece of history. Understanding the story behind the piece, the sweat begins to bead on your forehead. “Could this be one of those?” you question yourself. The convincing thoughts race through your mind as you begin to dig through your wallet for the credit card thinking,“I am sure of it!”
Fighting back any thoughts of doubt, you hurriedly pay for the treasure. Once in your hands, you begin to begin to examine the details. The doubts come rushing back along with the possibility that regret will soon follow. This scenario is bound to happen, even to the most seasoned experts. Eventually, every collector will experience the letdown upon the discovery that they rushed into a purchase ignoring all the education and experience that would have protected them from buying a fake.
My experience came last year when I spotted a much coveted Navy Expeditionary Medal with the rare Wake Island clasp affixed to the ribbon. The medal (with the clasp) was awarded only to those sailors and marines who served in defense of Wake Island in December, 1941 from the 7th to the 22nd.
More than 450 Marines and nearly 70 naval personnel bravely repelled multiple Japanese aerial and naval bombardments and landing assaults as the Japanese attempted to wrest the island away from the U.S. forces. Severely outnumbered more than five to one, the Americans finally surrendered Wake to the enemy. Suffering 120 killed in action and 50 wounded, the Americans inflicted heavy losses on the Japanese forces sinking two destroyers and two patrol boats as well as heavily damaging a light cruiser. Japanese landing forces suffered 820 killed and more than 330 wounded in action.

My 1950s HLP-made Navy Expeditionary Medal with the fake Wake Island clasp.
My “fake” medal consists of a late 1950s authentic Navy Expeditionary medal with HLP (for the maker, His Lordship Products, Inc.) stamped into the rim of the planchet. The details of the strike are quite fine and even the most subtle areas of the design are quite crisp. The planchet is significantly thicker than a modern strike and is devoid of the modern synthetic antiquing. The brooch indicates that it is from the late ‘50s to early ‘60s.

To compare, this Wake Island clasp for the Navy Expeditionary Medal appears to be authentic. Note the crisp lettering and sharpness to the detail of the rope-border (source: eBay image).
Where the trouble with this medal starts to surface is with close examination of the Wake Island clasp. Ignoring the Rube Goldberg hack-job on the reverse (which can be overlooked…I have seen other claps butchered, although not quite as bad as this), the face is where I should have focused my initial attention.
- Showing the detail of the “WAKE” lettering and border (source: eBay image).
- Note the crisp lettering and the rope border (source: eBay image).
- The back side of the Wake Clasp (source: eBay image).
Upon a close examination of the field (of the clasp), I noticed the bumpy surface between the lettering and the edge where it should have been smooth. I also noticed that the lettering and the rope-design that surrounded the face all looked blurry or soft (as opposed to being crisp and sharp). All of these issues should have set off alarm bells in my head. All of these discernible issues indicate that the clasp was a forgery – a product of sand mold-casting, which is a cheap reproduction method that is routinely employed in these forgeries.
I will chalk this episode up as a lesson learned. I am keeping this medal in my collection as both a reminder and a nice “filler” as I will probably never be able to afford an authentic example. Everything else about the medal, suspension and clasp is makes this an otherwise very nice example of an early Navy Expeditionary Medal.
Answering the Call of Remembrance Through Collecting

The line to get inside the Alamo is typically long but it does move quite fast. It is odd to see the city tower above the 18th Century structure.
There is no doubt that social media and news outlets will be dotted with posts and stories marking the 76th anniversary of the Day of Infamy – the Japanese sneak attack on Pearl Harbor and the surrounding military installations on the Island of Oahu – throughout this day. Though, I wonder if our nation’s youth are on the verge of forgetting about this event as we are losing sight of other terrible events that were perpetrated upon our citizens. Fortunately, forgetting about Pearl Harbor hasn’t quite happened yet as there are still WWII veterans, specifically Pearl Harbor Survivors remaining among us.
In the United States’ past history with such events, the meanings behind rallying cries such as “Remember the Alamo” and “Remember the Maine” are nearly lost to history. While visiting San Antonio this past summer, my family toured the Alamo and revisited the story of the siege and the ensuing battle that left no survivors among those who were defending the mission and fort. Without getting to far off track, the somberness of in the feeling one receives when walking through the building and the grounds is palpable but not the same as what is experienced when standing on the deck of the USS Arizona Memorial. Not too far from my home lies a monument – a memorial of sorts – from the USS Maine; the disaster that became the catalyst that propelled the United States into a war with Spain in 1898. This monument, a mere obelisk with naval gun shell mounted atop is easily overlooked by park visitors as it is situated a considerable distance from other attractions within the park. Remember the Maine?
- This monument to the USS Maine resides in Tacoma, Washington’s Point Defiance Park.
- The Point Defiance monument to the USS Maine was dedicated to the sailors of the Maine and to the Spanish American War veterans.
- The well-weathered granite base and projectile (from the Maine) is tucked away inside Point Defiance Park in Tacoma, Washington.
- This is one of five such monuments (from the Maine’s main battery) that are located throughout the United States. This is a 10-inch projectile that was removed from the raised wreckage of the ship.

The USS Arizona Memorial is situated on piers astride of the wreckage of the ship. The barbette of turret #3 is visible.
Visiting such locations always presents opportunities for me to learn something that I didn’t know before – details that one cannot grasp with the proper context that resides within the actual location of the event that took place there. Even though I had previously visited the Alamo (when I was very young), I had no memories of it and the entire experience was new and overwhelming. In contrast, the last visit that I made to the USS Arizona Memorial was my fourth (and the first with my wife) and I was still left with a new perspective and freshness of the pain and suffering that the men endured as their ships were under attack or while they awaited rescue (some for days) within the heavily damaged or destroyed ships. Unlike the Alamo, when one steps foot on the Arizona Memorial, they are standing above more than a structure that was once a warship of the United States. Beneath the waves and inside the rusting hulk are more than 1,100 remains of the nearly 1,200 men who were lost when the ship was destroyed.

Emerging from the waves are a pair of bollards from the starboard side of the forecastle of the wreckage of the USS Arizona, visible from the memorial.

This piece of the USS Arizona is on display at the Indiana Military Museum.
Interest in the USS Arizona (and the attack on Pearl Harbor in general) remains quite considerable for most historians. For militaria collectors, the passion to preserve the history of the ship and the men who perished or survived the ship’s destruction continues to increase. When any item (that can be directly associated with a sailor or marine who served aboard her) is listed at auction, bidding can happen at a feverish rate and the prices for even a simple uniform item can drive humble collectors (such as me) out of contention. Where the prices become near-frightening is when the items are personal decorations (specifically engraved Purple Heart Medals) from men who were killed in action aboard the ship on that fateful day. While any Pearl Harbor KIA grouping receives considerable attention from collectors, men from the Arizona are even more highly regarded. It is an odd phenomenon to observe the interest that is generated, especially when the transaction amounts are listed. While I certainly can understand the interest in possessing such an important piece of individual history, I am very uneasy when I see the monetized aspect of this part of my passion.
- When I see one of these posthumous Purple Heart Medals such as this one that was awarded to Seaman First Class Huys’ family, I cannot help but sense the pain of loss that was experienced by his parents when they first learned of the attack and that their son was among those who perished (image source: US Militaria Forum).
- Another posthumous Purple Heart Medal from an Arizona sailor, Radioman 3/c Otis Dennis (image source: US Militaria Forum).
- Electrician’s Mate second class Harold B. Wood’s Purple Heart and Good Conduct Medals. EM2/c Wood was killed aboard the USS Arizona on December 7th, 1941 (image source: US Militaria Forum).
- Apprentice Seaman Thomas Hembree was awarded his Purple Heart Medal posthumously having lost his life aboard the USS Arizona during the Japanese attack (image source: US Militaria Forum).
- Chief Watertender William Tisdale’s posthumous Purple Heart Medal (image source: US Militaria Forum).
Not wanting to focus on the financial aspects or my personal concerns regarding medals that are awarded to the surviving families, I have seen many collectors who painstakingly and beautifully research and preserve the personal stories of each sailor who was lost and for that individual’s specific medal. A handful of these collectors display these medals and personal stories with the general public which, I suppose can be likened to a traveling memorial to the service members who made the ultimate sacrifice. Without seeing such displays, it is very difficult to understand the magnitude of the personal sacrifices that are made by those who serve in the armed forces.

This group from a USS Arizona survivor contains the sailor’s photo album and distinguishing marks from his uniform (image source: US Militaria Forum).
Within my own collection are two photographs of the USS Arizona that were part of my uncle’s collection from when he served aboard three different battleships (Pennsylvania, Tennessee and California) during his navy career (from 1918-1929), all three ships that were later present when the Japanese attacked on December 7th, 1941. While I am certainly interested in the preservation of the history of this day, seeking Pearl Harbor or more specifically, USS Arizona pieces is not something that I am interested in with my militaria collecting. Instead, I spend time reflecting on what the service members within the ships, at the air bases and the citizens surrounding Oahu must have endured during the hours of the days, weeks, months and even years following the attacks.

One of two photos from my uncle’s navy photo album shows the USS Arizona transiting the Panama Canal.
Remember Pearl Harbor! Remember the Arizona!
For more on militaria mollecting of these significant events, see:
- A British Collector of the Alamo – Foreign Collectors of American Militaria
- Remembering (and Collecting) the USS Maine!
- A Piece of the Day of Infamy or Simply a Connection to an Historic Ship?
Historic Group Spotlight: Naval Aviator who Spotted and Maintained Visual Contact of the Bismarck
Most of the militaria and artifacts that I write about are pieces that are in my collection or are historical events that have some sort of personal context or connection. There are times, however that I find myself absolutely fascinated with artifacts in others’ collections that have me absolutely captivated. The subject of my efforts in this piece has me captivated both by the items and their original owner’s participation in history.

U.S. naval aviator, Carl Rinehart in the co-pilot seat during World War II (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
Militaria collecting, for me and many other collectors, is about the history. More specifically, it is about the individual and personal connections to historical events. For collectors, seeking out and acquiring artifacts from veterans who participated in pivotal or notable events helps to breathe life into what can otherwise be, for much of the population, a mundane event from the past.
The average American fan of World War II history is familiar with events tied to the more obvious specific dates: December 7, 1941, June 6, 1944 or perhaps even, August 6, 1945. For those of you who might need some hints as your morning coffee or tea has yet to take effect: Pearl Harbor, D-Day and Hiroshima. Most people know about specific campaigns and battles such as Iwo Jima, Midway, Operation Overlord and the Battle of the Bulge.
Considering those details, how many Americans are familiar enough with history to understand that World War II was being fought in Europe for nearly two years prior to the United States Congress’ war declaration on December 8th? For that matter, war was in full swing in Asia for almost five years by December of 1941. With this in mind, how many of the American public understand that though the U.S. was abstaining from the war and clinging to the isolationist stance, U.S. servicemen were, in fact, active and serving in both the Pacific and European theaters?
Perhaps one of the most significant naval pursuits (culminating in two significant battles) during those early years of WWII surrounds the engagement between the navy of Great Britain and the German Kriegsmarine that spanned six days in May of 1941. A prevalent and familiar battle cry that still resonates from that time was the call to “Sink the Bismarck” as the British sought to both avenge the loss of the HMS Hood (at the Battle of the Denmark Strait on May 24, 1941) and prevent the German ship from succeeding in her mission to disrupt the transatlantic shipping lifeline from North America (Operation Rheinübung). The Royal Navy ultimately prevailed in her mission, ending the German battleship’s short-lived career with the effective employment of carrier-based aircraft to disable the ship followed by naval gunfire to send her to the bottom on May 27.

Bismarck after her breakout steams near Iceland prior to the Battle of Denmark Strait, 1941.
These naval battles between our ally and the Germans are the subject study by historians and military strategists alike and are frequently popularized with articles, books and television programs, keeping the history on the forefront of cultural heritage on both sides of the Atlantic. But one fact that is seldom discussed is that American naval aviators played a small role in the Royal Navy’s open-ocean victory.
In the early years of Britain’s war with Germany, the U.S. was providing assistance in their fight by sending supplies (food, fuel and military equipment) across the ocean in large convoys. Recognizing the significance of that vital lifeline, the Germans re-employed and improved upon a WWI tactic of utilizing submarines (U-boats) in “wolf-packs” to destroy, or at least, disrupt the movement of the convoys, sending thousands of tons of merchant ships to the ocean bottom. In response, the U.S. began supplying Britain with long-range patrol and bomber aircraft providing an effective counter-tactic, protecting the convoys from the subsurface threats.
Just weeks prior to the Bismarck engagements, the Royal Air Force began taking delivery of American-supplied PBY Catalina flying boats. To expedite training of the RAF flight crews on their new aircraft, the U.S. Navy also sent their own support crews and aviators. Despite the U.S. neutrality at this point in the war, some U.S. Navy aircrews would support the RAF by flying patrol missions in the PBYs.
Days following the Denmark Strait engagement (and the loss of the battlecruiser Hood), a Consolidated-built PBY-5 Catalina departed Oban, Scotland on a patrol mission in search of the Bismarck. PBY “O” with Carl W. Rinehart in command, launched May 26 at 12:15pm on what would become a record-setting (for airborne length of time) and historic flight. Twelve hours later, Rinehart’s crew spotted the Bismarck steaming in the direction of occupied France (the ship had been spotted and position reported hours earlier by another U.S. Navy Catalina pilot, Ensign Leonard B. Smith). Dropping down for a closer look, the Catalina descended from the clouds into a firestorm of anti-aircraft gunnery from the enemy ship, and Rinehart and his co-pilot struggled to maneuver the flying boat to safety.
- The pinnacle of the Rinehart group – his naval aviator flight log books. It is fascinating to see such monumental historic moments on the pages of these logs (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
- Rinehart’s Flight Log – Entries for May, 1941. Note the entry with the red pencil encircling of two specific entries – the 26.2 hours of flight and the search for the Bismarck (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
- The entry for the May 26-27, 1941 Bismarck search mission that resulted in a record-setting flight for time in the air. It also resulted in locating the enemy ship and maintaining contact until she was sunk (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
Remaining in the vicinity of the Bismarck, Rinehart and his crew maintained visual contact with the ship observing the ensuing aerial torpedo assault by the Swordfish aircraft from the HMS Ark Royal on the evening of the 26th. Now with her rudders jammed, Bismarck was unable to continue her course to the safety of German air cover. Over the course of the night, the Royal Navy was able to draw in the attacking surface force and bring about the end of the Kriegsmarine’s pride. Catalina “O” and her crew were present, witnessing the entire last battle of the Bismarck. Low on fuel, Rinehart turned his plane on a heading to return to base. Touching down at 13:40 on May 27, his Catalina had been airborne for more than 26 hours of continual flight.
Rinehart would continue to serve throughout WWII and through the Korean War. He retired from the navy with the rank of captain having earned the Distinguished Flying Cross (not for the Bismarck patrol). Captain Rinehart passed away in 1996 at the age of 83 in Pensacola, Florida.
- Rinehart’s Photo Album Cover (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
- One of the images in Rinehart’s photo album showing a PBY Catalina, 31-P-21, in flight over Panama (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
- Rinehart Image – Lining up for a bombing run on an enemy train (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
- Another scan of a Rinehart Image of what appears to be an attack on a train(image source: Kurt Stauffer).
- One of Carl Rinehart’s photos of an aerial bomb exploding over a target. This image was probably taken, most likely, from Rinehart’s PBY (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
Years later, artifacts from his lengthy naval career surfaced at auction and one collector was fortunate to acquire several items, piecing together this well-rounded group that documents Captain Rinehart’s tenure. Among his decorations and ribbons are Rinehart’s service and campaign medals along with his DFC medal. There are also the usual rank devices and a nice set of gold naval aviator’s wings and other insignia devices all belonging to Rinehart.

This excellent collection of medals, devices and other personal pieces from Captain Rinehart’s naval service are a nice example of a WWII naval aviator’s service. As Rinehart served through the Korean War, he most certainly would have had additional medals and ribbons along with devices for his final rank. These pieces must exist in another collector’s possession (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
For me, the items that truly makes this group stand out are ephemera. This collector was able to obtain Rinehart’s spectacular photo album containing snapshots from his wartime service. While each of these images are one-of-a-kind and represent a seldom seen vantage point into the life of WWII decorated flying boat aviator, they still pale in comparison to the central, most historically significant aspect of Rinehart group, his flight log books.
- The first entry on this page sums up the historic day, the capitulation aboard the USS Missouri by the Japanese (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
- Rinehart noted that the Japanese had agreed to the unconditional surrender terms of the Allied forces (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
- A page from Rinehart’s Photo Album (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
- Rinehart Image – Performing Maintenance on the PBY’s vertical stabilizer (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
Thumbing through the pages, there are significant events noted by Rinehart among his various flights and missions including, “Peace Signed Aboard BB USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay V-J Day.” Capping off the log entries is one particular flight with mention of the Bismarck search circled in red colored pencil and the take-off/landing times.

Rinehart’s PBY Crew somewhere in the South Pacific during World War II (image source: Kurt Stauffer).
While a grouping from Rinehart’s more notable colleague, Leonard Smith, might bring more attention and monetary value, this group is no less historically significant.
(All photos depicting the Carl Rinehart collection are courtesy of Kurt Stauffer unless otherwise noted)