Category Archives: World War I
Consistency through Change – The U.S. Army Uniform

This uniform, though an immediate post-Civil War-issue, is clearly that of a sergeant in the U.S. Cavalry as noted by the gold chevrons (hand-tinted in the photo).
Over the weekend leading up to Independence Day, I had been inspired by my family military service research project, which had me neck-deep in the American Civil War, which caused me to drag out a few DVDs for the sheer joy of watching history portrayed on the screen. Since the Fourth of July was coming up, I wanted to be sure to view director Ronald Maxwell’s 1993 film Gettysburg, on or near the anniversary of the battle, which took place on July 1-3, 1863.
I had watched these films (including Gods and Generals and Glory) countless times in the past, but this weekend, I employed more scrutiny while looking at the uniforms and other details. Paying particular attention to the fabrics of the uniforms, I was observing the variations for the different functions (such as artillerymen, cavalrymen, and infantry) while noting how the field commanders could observe from vantage points where these regiments were positioned, making any needed adjustments to counter the opponents’ movements or alignments. For those commanders, visual observations from afar were imperative and the uniforms (and regimental colors/flags) were mandatory to facilitate good decision making.
The tactics employed for the majority of the Civil War were largely carryovers from previous conflicts and had not kept pace with the advancement of the weaponry. Armies were still arranged in battle lines facing off with the enemy at very close range (the blue of the Union and the gray of the Confederacy), before the commands were given to open fire with the rifles and side arms. The projectile technology and barrel rifling present in the almost all of the infantry firearms meant that a significantly higher percentage of the bullets would strike the targets. In prior conflicts where smooth-bore muskets and round-ball projectiles were the norm, hitting the target was met with far less success.
The uniforms of the Civil War had also seen some advancement as they departed from the highly stylized affairs of the Revolution to a more functional design. In the years following the war, uniform designs saw some minor alterations through the Indian Wars and into the Spanish American War. By World War I, concealment and camouflaging the troops started to become a consideration of military leadership. Gone were the colorful fabrics, exchanged for olive drab (OD) green. By World War II, camo patterns began to emerge in combat uniforms for the army and marines, though they wouldn’t be fully available for all combat uniforms until the late 1970s.
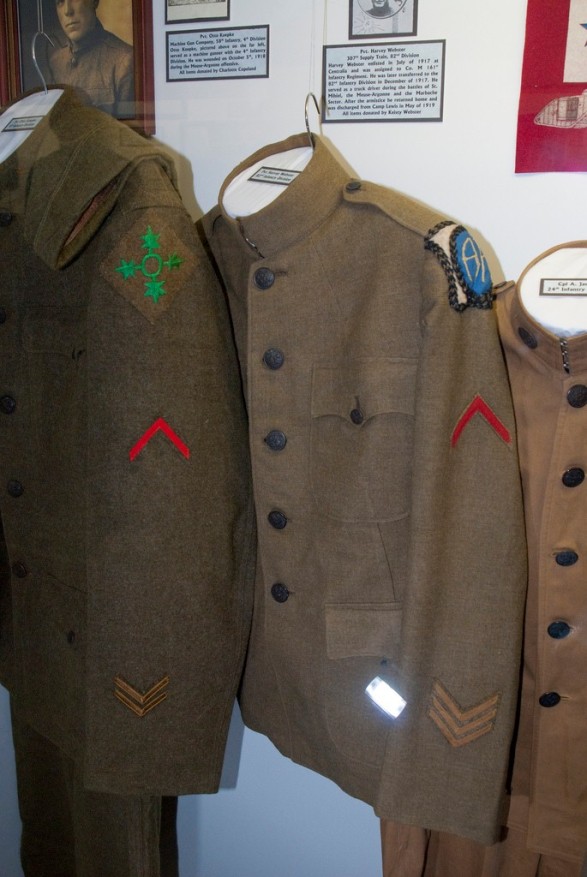

Though these uniforms have a classy appearance, they were designed for and used in combat. Their OD green color was the precursor to camouflage.

This World War II-era USMC combat uniform top was made between 1942 and 1944. Note the reversible camo pattern can be seen inside the collar (source: GIJive).
For collectors, these pattern camouflage combat uniforms are some of the most highly sought items due to their scarcity and aesthetics. The units who wore the camo in WWII through the Viet Nam War tended to be more elite or highly specialized as their function dictated even better concealment than was afforded with the OD uniforms worn by regular troops.
Fast-forward to the present-day armed forces, where camouflage is now commonplace among all branches. The Navy, in 2007-2008, was the last to employ camo, a combination of varying shades of blue, for their utility uniforms citing the concealment benefits (of shipboard dirt and grime) the pattern affords sailors. All of the services have adopted the digital or pixellated camo that is either a direct-use or derivative of the Universal Camouflage Pattern (UCP) first employed (by the U.S.) with the Marine Corps when it debuted in 2002. Since then, collectors have been scouring the thrift and surplus shops, seeking to gather every digital camo uniform style along with like-patterned field gear and equipment.

The first of the U.S. Armed Forces to employ digital camouflage, the USMC was able to demonstrate successful concealment of their ranks in all combat theaters. Shown are the two variations, “Desert” on the left and “Woodland” on the right.
 After a very limited testing cycle and what appeared to be a rush to get their own digital camo pattern, the U.S. Army rolled out their ACU or Army Combat Uniform with troops that were deploying to Iraq in 2005. With nearly $5 billion (yes, that is a “B”) in outfitting their troops with uniforms, the army brass announced this week that they are abandoning the ACU for a different pattern citing poor concealment performance and ineffectiveness across all combat environments. With the news of the change, the army has decided upon the replacement pattern, known as MultiCam, which has already been in use exclusively in the Afghanistan theater.
After a very limited testing cycle and what appeared to be a rush to get their own digital camo pattern, the U.S. Army rolled out their ACU or Army Combat Uniform with troops that were deploying to Iraq in 2005. With nearly $5 billion (yes, that is a “B”) in outfitting their troops with uniforms, the army brass announced this week that they are abandoning the ACU for a different pattern citing poor concealment performance and ineffectiveness across all combat environments. With the news of the change, the army has decided upon the replacement pattern, known as MultiCam, which has already been in use exclusively in the Afghanistan theater.
For collectors of MultiCam, this could be both a boon (making the items abundantly available) and a detractor (the limited pattern was more difficult to obtain which tended to drive the prices up with the significant demand). For those who pursue ACU, it could take decades for prices to start climbing which means that stockpiling these uniforms could be a waste of time and resources. Only time will tell.
Since the Civil War, the U.S. Army uniform has one very consistent aspect that soldiers and collectors alike can hang their hat upon…change.
I am an American Veteran with Canadian Military Heritage
I’ve been revisiting my family tree research, spurred on by catching up on watching episodes of The Learning Channel’s Who Do You Think You Are? (WDYTYA) The show follows a pretty simplistic theme of tracing some Hollywood notable’s ancestral history as they have been suddenly overcome with desire to know where they came from. There is always some sort of misplaced desire for self-validation as they seek to identify with the very real struggles that someone in their family tree endured centuries ago. In watching them I often find the humor as the celebrity emotionally aligns with a nine or ten times great grandparent as if that person were an active part of their life. Where the humor in this originates is that one must consider exactly how many great grandparents one has at this particular point in our ancestry.
My 3x great grandfather (one of sixteen such 3x great grandfathers) served with the 6th Pennsylvania Cavalry during the American Civil War) and like the Hollywood celebrities on WDYTYA, I have researched him extensively and I do identify with him. But consider that there are 15 other 3x great grandfathers along with eight 2x greats, four greats and two grandfathers. That means that five generations above me encompass 28 grandfathers including the lone Civil War veteran that I thoroughly researched. If viewed this prospective with another one of the great grandfathers (whom I researched and found to have served during the American Revolution), he would be one of 64 5x great grandfathers (for a total of 254 total grandfathers at this generation-level). This can get confusing to grasp without a visual:
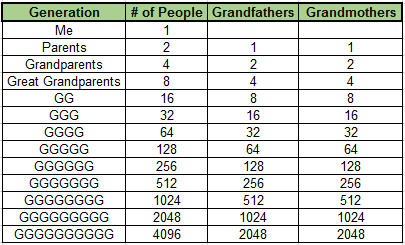
When folks refer to their 7th great grandfather, what does that mean? Did they have more than one? The answer is that everyone has 256 7th great grandfathers. It is simple math, folks!

There are a few other pieces that I have for the display that I am assembling, including a section of vintage ribbon for the service medal. The shoulder tabs are a more recent acquisition as is the CFC hat badge (bottom left) that my 2x great grandfather wore prior to being assigned to the 230th. The two smaller insignia flanking the medal were worn on the uniform collar. The pin on the lower right was a veteran’s organization pin.
I have been gathering artifacts together to create representations of some of my ancestors with military service. I have been sporadically researching as many relatives as I can locate to document a historical narrative of service by members of my family. This is a daunting task considering how many direct ancestors I have and I have been also including some uncles and cousins as I uncover them. One of my 2x great grandfathers (one of 8 such great grandfathers) was a British citizen who emigrated to Victoria, British Columbia with his wife and ten children a few years following the turn of the twentieth century. By the time the Great War broke out in Europe in 1914, he was a 45-year-old carpenter and home builder. When he was drafted into the Forestry Corps of the Canadian Expeditionary Force (CEF) in June of 1916, he was 47 and a widower. He served in Europe for the duration of the war harvesting timber for use in the war effort, plying his carpentry skills in some fashion being far too old for combat duty.
Having a Canadian veteran ancestor (one of two – I wrote about the other one, previously) posed some challenges in researching his service as nearly every aspect of research is different from what I am familiar with (with American military records). Learning the terminology and the unit structure was difficult but even more challenging was deciphering my GG grandfather’s service records let alone locating details as to what his uniform insignia and devices would have been. Thanks to a few helpful CEF sites and forums, I was able to piece together some of the principle elements in order to assemble a shadow box at some point in the future.

This is a simple, yet tasteful display of a veteran of the 230th Canadian Forestry Corps from WWI. This soldier was in the same unit as my 2x great grandfather.
As any Canadian militaria collector could tell you, locating pieces from individual regiments/units of the Forestry Corps can be daunting. When I started on this path a few years ago, the prices were higher than those of American units by as much as three times. Collar and cap devices and badges were can reach prices beyond $40-50 (collar) and $70-100 (for caps badges). Not that ever intended to purchase actual uniforms pieces (tunic, cap, hat, etc.), I still maintained a watchful eye just to see what might show up for sale. Today, my eyes were enlarged and mouth left agape when something appeared in my automated search for such items.
Listed yesterday on eBay was a 1917-dated British trench hat that is in impeccable condition, complete with the badge of my 2x great-grandfather’s unit. Everything about this century-old cap seems to be in an incredible state – the hat’s shape, the leather sweatband – all of it. But then I saw the opening bid amount – $750.00 (in USD) – and immediately, my jaw struck my desktop beneath me! In the “People who viewed this item also viewed” section were British head covers (one trench hat and two visor caps) of comparable condition but with devices from other, non-Forestry units with prices that ranged from $500-700, depending upon the unit insignia. The hat from my ancestor’s unit topped the range of prices. Being in possession of the cap device, I wouldn’t need to pursue such an expensive purchase (I don’t need the hat for the display that I am assembling) so I will simply watch to see if the hat does end up finding a new home and take note of the selling price.
- This hat differs from the peak cap in that the top is slouched down over the sides and the bill is soft and stitched like a baseball cap. The 230th Canadian Forestry Corps device is centered over the leather chinstrap (eBay image).
- Showing the hat’s right side and the top of the visor (eBay image).
- The close up of the CFC badge – the insignia incorporates crossed pikes superimposed over a maple leaf with a long crosscut saw with a beaver (eBay image).
- The chinstrap button detail is impressive (eBay image).
- The high-level view of the hat’s underside (eBay image).
- These markings appear to be the maker’s mark, the hat’s size and the date of manufacture (eBay image).
- I am unfamiliar with these markings. I am sure that the experienced collectors and historians could easily provide some insight as to their meaning (eBay image).
- On the sweatband, the soldier’s initials and service number are hand-inscribed and provide an easy path for researching the original owner’s service (eBay image).
With just one of my maternal 2x great grandfathers with military service (albeit, British-Canadian) and none of my paternal 2x great grandfathers, I don’t have any more military artifacts left to gather for this particular generation (unless I am able to discover new facts for others). The preceding and following generations reveal that I have a lot of research effort in store for me not to mention what lies ahead for me within my wife’s equally extensive family military history.
See Also:
Lumbering Along: Collecting C.E.F. Forestry Militaria
A Bullet with No Name
Most people who know me would agree with the statement that I take pleasure in the obscurity and oddities in life. If there is any sort military or historic significance, my interest is only fueled further.
Militaria collectors have heard the same story told countless times by baffled and befuddled surviving family members – the lost history of an object that (obviously) held such considerable personal significance that a veteran would be compelled to keep the item in their inventory for decades. For one of my veteran relatives, that same story has played out with an item that was in among the decorations, insignia and other personal militaria, preserved for fifty-plus years.
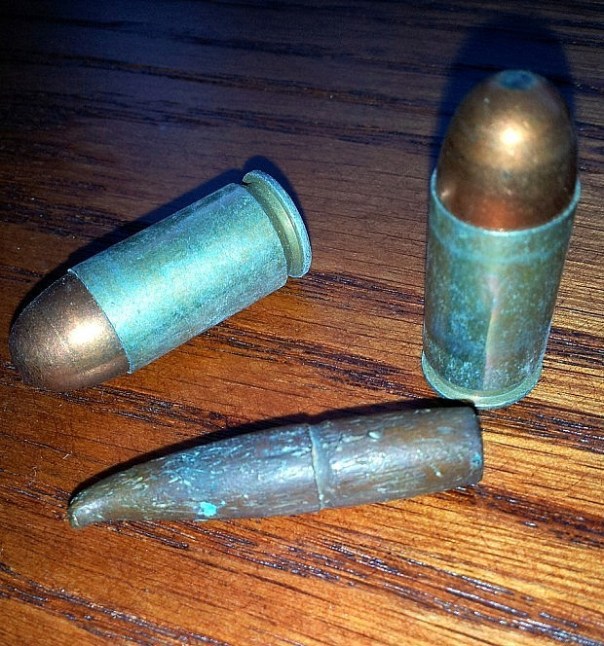

The crimp ring around the middle of the bullet’s length shows where the top of the bullet casing was pressed against the projectile. When compared to these WWII .45cal rounds, it becomes apparent that the bullet is in the 7mm bore size-range.
When I received the box of items, I quickly inventoried each ribbon, uniform button, hat device and accouterments that dated from his World War I service through the Korean War. The one item that caught me by surprise was a long, slender lead projectile with a mushed tip.

They are difficult to make out with the naked eye, but the markings are “A-T-S” and “L-V-C”. The character in the center doesn’t appear to be a character at all.
It was clear that this blackened item was a small arms projectile. Based on size comparison with 9mm and 7.62 rounds, it was more along the lines of the latter, but it was clearly not a modern AK/SKS (or other Soviet-derivative). Perhaps it was a 7mm or smaller round? Without any means to accurately measure the bullet, I cannot accurately determine the bore-size or caliber. I’ll have to leave that for another day.
Further examination of the object proved to me that it was bullet that had been fired and had struck its target, causing the tip to blunt. While I am not a ballistics expert, I have seen the markings that firing makes on a bullet. This round clearly has striations that lead me to believe that it has traveled the length of a rifled barrel. It also possesses a crimping imprint, almost at the halfway-point on the projectile.
So what does all this information mean? Why did my uncle hang on to it for all those years? Had this been a bullet that struck him on the battlefield? Had it been a near miss?
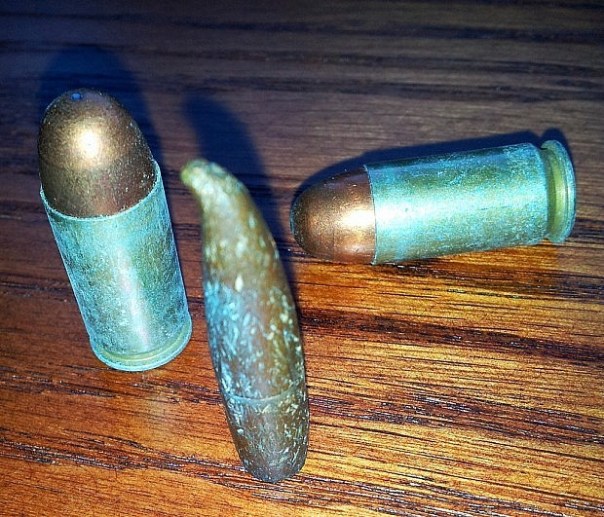

In this view, the mushed tip is easily seen, as are some of the striations.
My uncle passed away 20 years ago and the story surrounding the bullet sadly died with him. Since he bothered to keep it, so will I along with other pieces in a display that honors several of my family members’ service.
Combat Medical Blades – Bolo Knives

Indiana Jones faces off with a sword-wielding opponent on the streets of Cairo in Raiders of the Lost Ark (source: Paramount Home Entertainment (Firm). (2008). Raiders of the lost ark. Hollywood, Calif: Paramount Home Entertainment).
When confronted by a henchman in a scene from the film, Raiders of the Lost Ark, Indiana Jones (played by Harrison Ford) notices the fancy blade-wielding skills of his opponent. Unimpressed by the acrobatics and the fancy blade-twirling bad-guy, Indy retrieves his revolver from his holster firing a single, well-placed shot, dropping the adversary nonchalantly.
I don’t profess to have knowledge of the type of sword wielded by unimportant character in that film nor do I have expert knowledge in the field of military edged weaponry. What I do have in my scabbard is the ability to use the research tools at my disposal – which comes in quite handy when given an arsenal of knives, swords, bayonets and bolo knives.
A few years ago, I was asked to catalog and obtain value estimates of some militaria pieces that were part of a family member’s collection. He had passed away some time before and his executor was carrying out the responsibilities of handling the estate. In the previous years, I had only seen a few items from the collection so I was surprised when I saw what was there for me to review. After completing my work on behalf of the state, I later learned that I was to receive some of the pieces that I had appraised, much to my surprise.
Of the blades I had inherited, three were quite unique, different from the rest of the pieces. Two of the three blades were almost identical in form and the other was a slight departure from the others. What set these blades apart from the rest was machete-like design with more size toward the end of the blade, giving the blade a bit of weight toward the end of the blade rather than at the center or toward the hilt. The design of these blades were fashioned after the weapon of choice of the Filipino resistance fighters from the revolt that started at the end of the Spanish-American war in 1898.
Known simply as bolo knives, the U.S. military-issue blades were less weapon and more utilitarian in function.
- The unique brass belt hanger of the leather-clad scabbard is much different from most WWI web gear attachments.
- The M1904 hospital corps bolo with its unique s-shaped brass hilt.
Now in my collection, the oldest of the three knives is the M1904 Hospital Corps Knife. Though many people suspect that the broad and heavy blade was important to facilitate field amputations, this thought is merely lore. Along with the knife is a bulky, leather-clad scabbard with a heavy brass swiveling brass belt hanger. My particular example is stamped with the date, “1914” which is much later in the production run. The M1904 knives were issued to field medical soldiers as the United States entered World War I in 1917.
The second knife is less bolo and more machete in its design. The M1910 bolo was designed and implemented for use as a brush-clearing tool. Some collectors reference the M1910 as a machine-gunner’s bolo as it was employed by the gun crews and used to clear machine gun nests of foliage and underbrush. My M1910 bolo is date-stamped 1917 and includes the correct leather-tipped, canvas-covered wooden scabbard.
- This 1944-dated USMC bolo and scabbard are a cherished part of my collection.
- The blade and hilt of the USMC World War II bolo.
The last bolo in my collection is probably the most sought-after of the three examples. Stamped U.S.M.C. directly on the blade, these knives were issued to U.S. Navy pharmacist’s mates who were attached to U.S. Marine Corps units. This detail leads many collectors to improperly conclude that the markings on the blade clearly indicate that the knives were made for the Marines. While this is indirectly true, the U.S.M.C. markings represent the United States Medical Corps, a branch of the U.S. Navy. On the reverse side, the blade is date-stamped, “1944” making the blade clearly a World War II-issued knife.
Although the blades are relatively inexpensive, they are considerably valuable to me as they come from a family member’s collection and were handed down to me. Though I do not have a desire to delve too far into edged weapons-collecting, I added to my collection by acquiring a pair of US Navy fighting knives to round out my collection. In future posts, I will cover these two types of knives, swords and sabers and even a few bayonets.

















